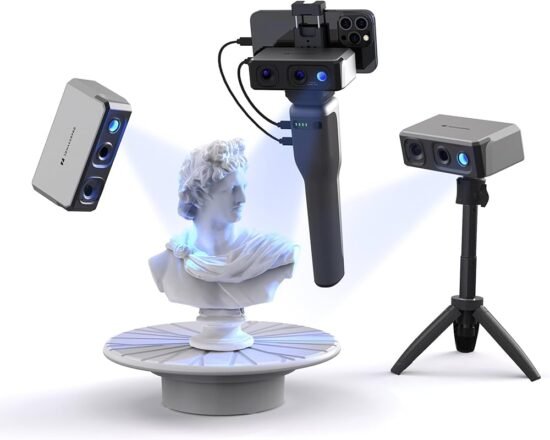
A 3D scanner is a device that uses various technologies to create a three-dimensional model of an object or surface. Here are examples of the most common scanning methods:
- Structured Light Scanning: The scanner projects structured light onto an object and then measures changes in that pattern on the object. Using this data, you can recreate a 3D model of the object.
- Laser Scanning: In this case, a laser beam is used to scan the object. The laser is reflected from the object’s surface, and the scanner’s sensors measure the laser’s travel time, which allows it to determine its distance from the object’s surface. This data is then used to create a 3D model.
- Photogrammetry: This method uses photographs of the object from different angles. When scanning, the program’s algorithm compares features and details in all photographs and creates a 3D model of the object based on this data.
After the scanning process, the received data is processed by software, which creates an accurate 3D model of the object. This model can be further used for visualization, analysis or printing on a 3D printer.
Popular 3D Scanner Models
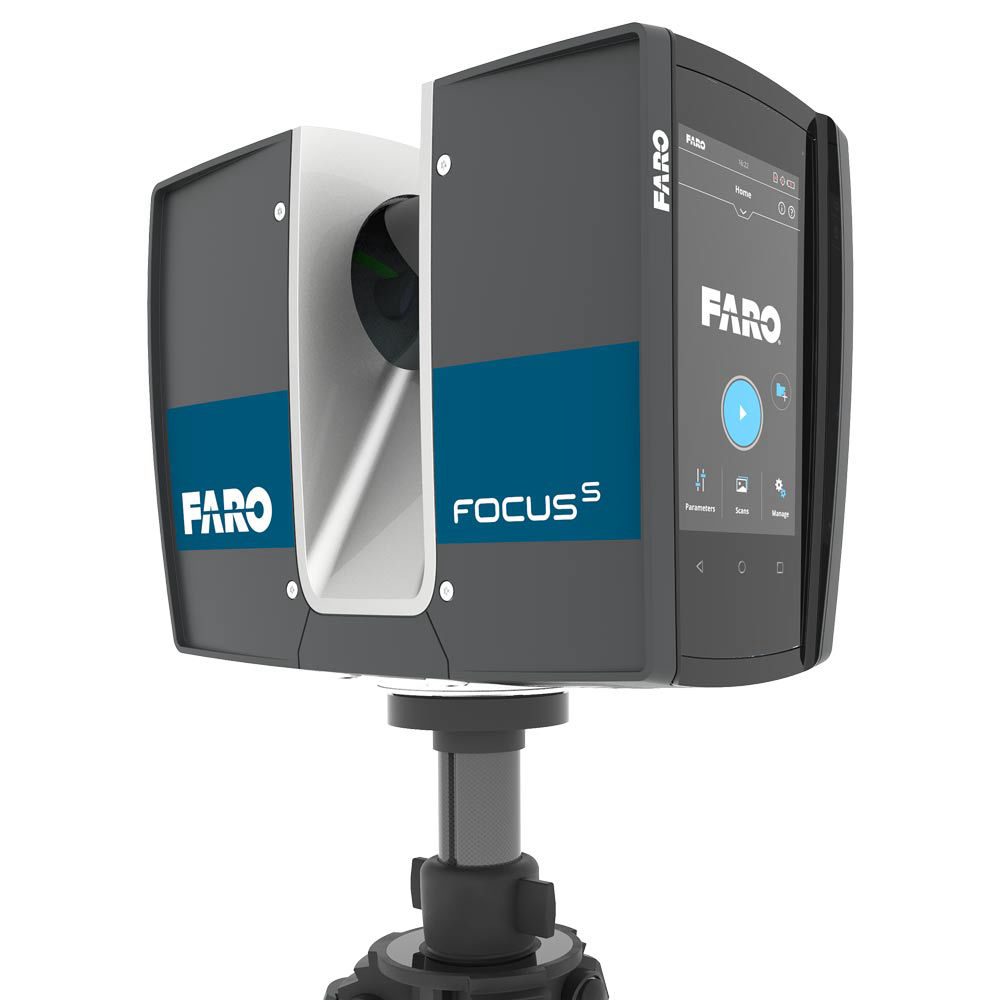
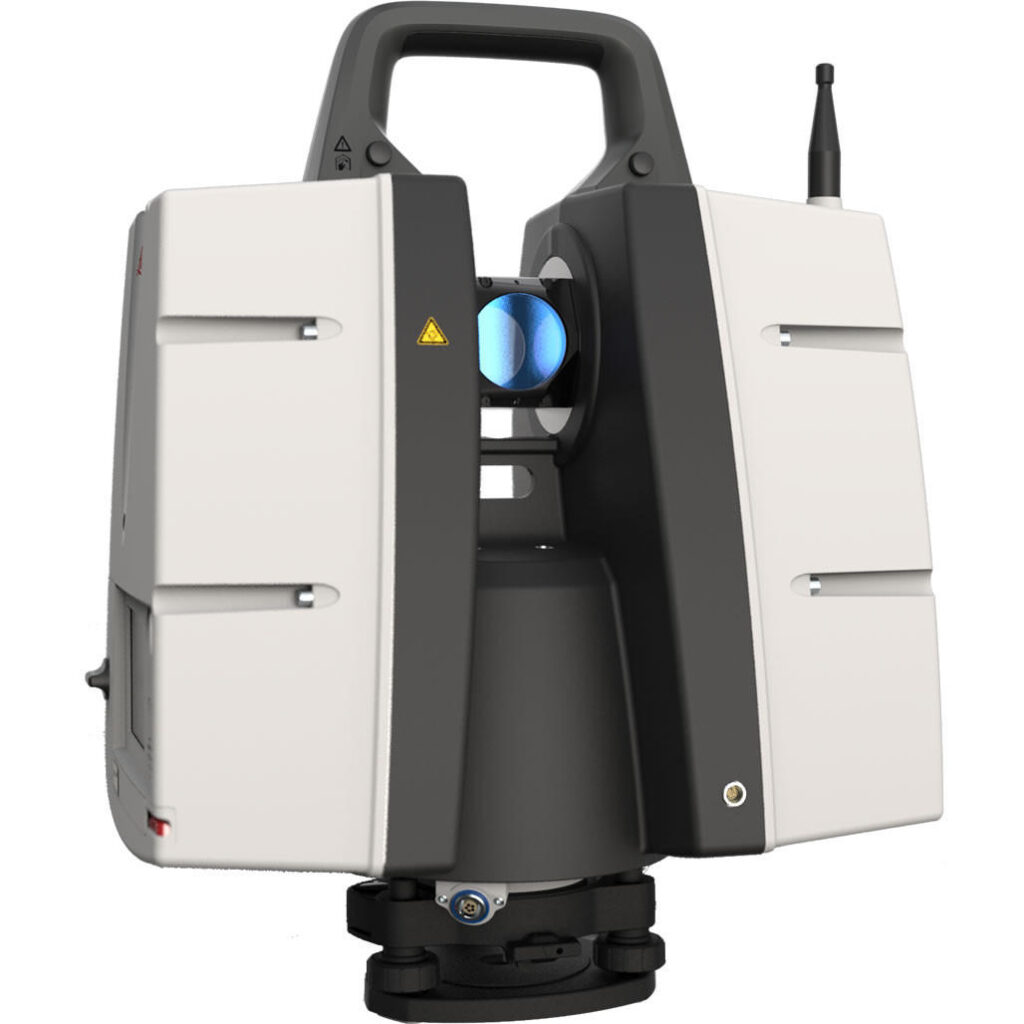
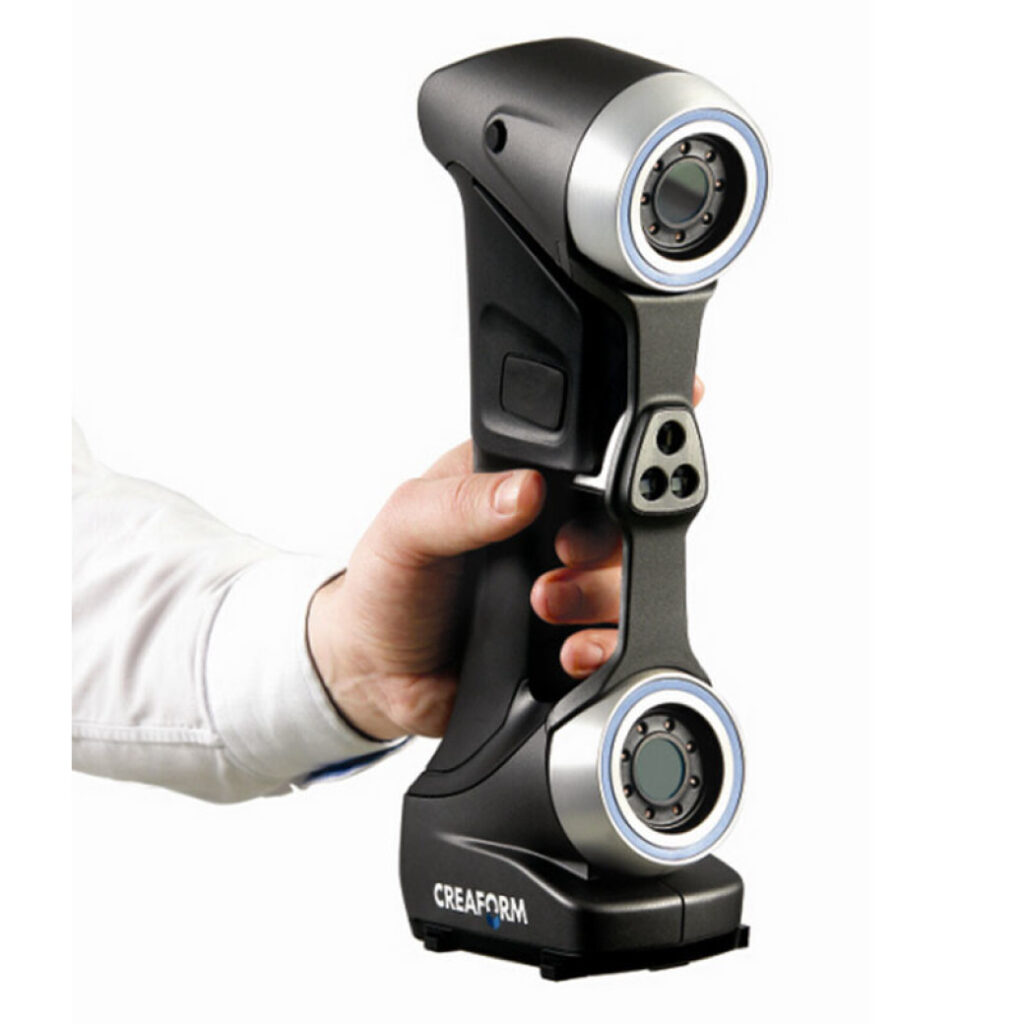




The preferred 3D scanner model depends on the specific requirements and goals of the user. However, there are several popular models that are generally considered to be market leaders:
- Faro Focus: This is an ultra-efficient and accurate scanner that can capture points up to 976,000 per meter. It also has a range of up to 330 meters and is capable of capturing color images.
- Leica Geosystems ScanStation: This is a survey-grade scanner with high accuracy and a range of up to 270 meters. It can also capture color images.
- Artec Eva: This is a portable and lightweight 3D scanner that provides high quality and accurate images. It has the ability to capture textures and color images.
- Creaform HandySCAN: This is a handheld 3D scanner with the ability to capture points with high precision. It is compact in size and easy to use.
These are just a few examples of popular models available on the market. It is important to choose the model that best suits the user’s requirements and budget.
Scanning Different Types of Materials


When scanning different types of materials with a 3D scanner, you need to know the following:
- Material Type: Different materials have different properties that can affect the scanning process and result. For example, metals can reflect light, which can cause problems with detecting surface texture, while transparent materials can create problems with reflecting the laser beam.
- Surface preparation: The surface of the object to be scanned must be clean and flat. Uneven surfaces, dust, or other contaminants may distort the scanned data. In some cases, it may be necessary to use special coatings or adhesives to improve scanning quality.
- Lighting: Lighting plays an important role in the scanning process. For best results, uniform and bright lighting is recommended to avoid shadows and reflections.
- Scanner Settings: Different types of materials may require different scanner settings. For example, to scan transparent objects you may need to increase the laser power or use additional filters.
- Data post-processing: After scanning, data processing may be required to remove noise, combine individual scans into a single object, or correct distortions caused by material properties.
It is important to remember that each 3D scanner has its own characteristics and manufacturer’s recommendations, so it is recommended that you read the documentation and user manual for your specific model before scanning different types of materials.
Costs

Costs for 3D scanning services can vary depending on several factors, including the complexity of the project, the size and complexity of the item, the required scanning accuracy and resolution, and the location of the firm providing the services.
Typically, the cost of 3D scanning is calculated individually for each project. It is recommended to get several quotes from different companies and compare their costs.
More complex and larger projects are expected to cost more as they require more time and resources to complete. In addition, if the site is located in a remote location, you may have to pay extra for transport and accommodation of specialists.
In general, the cost of a 3D scan can range from several hundred to several thousand US dollars depending on the factors above.
For Personal Use
Yes, there are now many different models of 3D scanners available on the market at different prices. Some of them are intended for separate use and allow you to create 3D models of objects for various purposes, for example, for printing on a 3D printer or for use in virtual reality. Prices for such scanners can range from several hundred dollars to several thousand, depending on their capabilities and quality. Therefore, if you are interested in purchasing a 3D scanner, it is recommended to study information about the available models and their functions in order to choose the appropriate option for your specific ones.
Common Difficulties

When purchasing a 3D scanner, a simple user may encounter the following difficulties:
- Wrong choice of scanner model: There are different models of 3D scanners with different functionality and capabilities. The average user may find it difficult to choose the right model that will suit his needs and budget.
- Incorrect installation and connection: Installing and setting up a 3D scanner can be difficult for the average user. An incorrect connection to the computer or an error in the software settings may result in the scanner not working.
- Incorrect use: The average user may face problems in using the 3D scanner correctly. Incorrect subject positioning, incorrect template overlay, or insufficient lighting can all result in unusable or poor-quality scanned models.
- Difficulty in processing and editing: The resulting scanned models may require additional processing and editing to become fully usable. The average user may need to learn specialized software to work with 3D models or hire specialists to perform these tasks.
- Limited scanner capabilities: The average user may encounter limited capabilities of the selected scanner model. Some scanners may have limitations on the size and type of objects scanned, as well as the detail and accuracy of the scan. This may limit the user’s ability to operate the 3D scanner.
Useful Tips
Here are some important tips for beginners working with a 3D scanner:
- Prepare the object: Before you start scanning, make sure that the object you want to scan is clean and does not have reflective surfaces that could distort the scan results.
- Use good lighting: Make sure the subject is well lit from all angles to avoid shadows and dark areas that could distort the scan.
- Hold the scanner carefully: Hold the scanner steadily and evenly when scanning to avoid blurry or distorted images. If a handheld scanner is used, make sure you keep it at a safe distance from the subject to avoid collision.
- Plan your scan: Determine in advance how many scan points you need to get the resolution and level of detail you need. Plan your scanning process in advance to save time and avoid mistakes.
- Use anchor points: If you have a complex or unstable object, you can use anchor points or markers to help the scanner track its position and maintain scanning accuracy.
- Check the results: Once the scan is complete, check the results carefully to make sure they meet your expectations. If something is wrong, you can try to scan again or use different settings.
- Practice: As with any skill, practice makes perfect. By gradually improving your 3D scanner skills, you will be able to achieve higher and higher scanning quality.
Don’t forget that working with a 3D scanner takes time and patience. Don’t be afraid to experiment and ask questions to improve your skills and achieve the best results.
Recommended Computer Requirements

The cost of a computer to run a 3D scanner can vary depending on your project requirements and budget. However, for a beginner, the following configuration is recommended:
- Processor: Intel Core i5 or AMD Ryzen 5
- RAM: 8 GB
- Graphics card: Nvidia GeForce GTX 1060
- Hard drive: 1 TB HDD or 256 GB SSD
- Operating system: Windows 10
- Monitor: 24 inches, resolution 1920×1080
The average cost of such a computer can range from $800 to $1200. However, the price may vary depending on the manufacturer and store chosen, as well as the availability of any additional components or peripherals.
Final Thoughts

When purchasing a 3D scanner, the user is advised to consider the following important steps:
- Determine your goals: Determine for what purposes you need a 3D scanner. This could be used in design and modeling, industrial manufacturing, medical or architectural sectors. This will help you choose the scanner that suits your needs.
- Budget: Set your budget for purchasing a 3D scanner. There are various scanner models in the market with different price ranges. It’s important to choose a scanner that fits your budget.
- Market Research: Conduct market research to identify different models and brands of 3D scanners. Compare their specifications, features, user reviews and prices.
- Support and Training: Make sure the company you purchase your scanner from offers support and training. Training may be required to use the scanner effectively and get the best results.
- Expandability: Consider expanding the scanner’s functionality in the future. Some scanner models offer software or hardware upgrades to improve functionality.
- Warranty and Service: Find out about your scanner’s warranty and service availability. This is important to ensure trouble-free operation and the ability to repair if necessary.
- Reviews and Recommendations: Read reviews and recommendations from other users who have already purchased this scanner. This will help you get an idea of the quality and performance of specific models.
- Demonstration: Ask the company from whom you are considering purchasing the scanner for the opportunity to test it or watch a demonstration of the scanner’s functions. This will give you an idea of its capabilities and uses.
Remember that each user may have individual needs and preferences when choosing a 3D scanner. Therefore, it is important to plan every step and make a decision based on your specific requirements and expectations.








