In the world of technology, where everything seems to be evolving at a breakneck speed, there’s one area that’s been capturing the imagination of engineers, designers, and even hobbyists alike: turning 3D scans into CAD models. It’s like turning a digital clay model into an intricate sculpture. But instead of a chisel and hammer, we use lasers and software. Now, if only Michelangelo had a 3D scanner, things might have been a tad easier for him!
The Marvel of 3D Scanning
3D scanning is essentially the process of analyzing real-world objects or environments to collect data on their shape and appearance. The collected data is then used to construct digital 3D models. Think of it as the digital equivalent of tracing an object. Instead of paper and pencil, we’re using lasers, structured light, or even photogrammetry. Now, if only my printer could scan and print a pizza in 3D—but that’s another conversation for another day.
Types of 3D Scanners
- Laser Scanners: These use laser beams to analyze an object’s surface. They’re precise and are often used in industries where detail is crucial. So, next time you see a laser, it could be scanning a car part rather than igniting a lightsaber.
- Structured Light Scanners: They project a series of light patterns on the object and capture how these patterns deform around the surface. This type of scanner is faster and often used for medium to large objects.
- Photogrammetry: This method uses photos taken from multiple angles to build a 3D model. Perfect for when you want to capture an entire vacation scene, including the sunburn you got on the beach.
The Transition to CAD Models
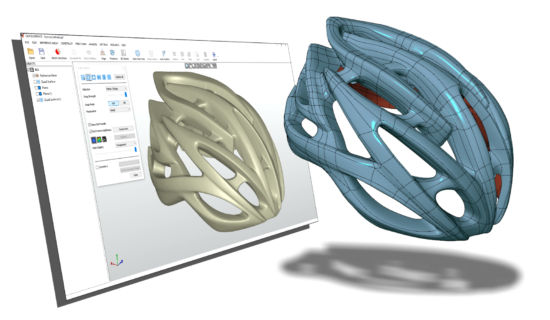
Once we have a 3D scan, the real fun begins—converting it into a CAD model. It’s like transforming a rough stone into a polished diamond. CAD, or Computer-Aided Design, involves using specialized software to create precision drawings or technical illustrations. These models can be used for anything from designing a new gadget to assembling a complex machine. If only it could help me design a fail-proof plan for assembling IKEA furniture.
Theoretical Underpinnings
The conversion from 3D scans to CAD models involves several theoretical considerations. Let’s delve into a few:
- Point Clouds: The data from 3D scans are often presented as point clouds. These are just a massive collection of points that represent the scanned object. It’s kind of like a constellation of stars, except these stars won’t help you navigate home.
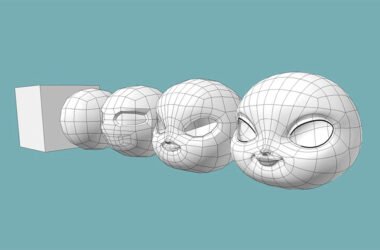
- Mesh Generation: A mesh is generated from the point cloud. This mesh is a collection of vertices, edges, and faces that define the shape of the 3D object. It’s like connecting the dots, except the dots are in three dimensions and require a bit more math.
- Surface Reconstruction: This step involves converting the mesh into a smooth surface. Imagine turning a pixelated image into a high-resolution photo. It’s all about making those sharp edges disappear like magic. Oops, I used the ‘M’ word!
The Practical Side of Things
Now, let’s get into the nitty-gritty of how this whole process works in practice. Turning 3D scans into CAD models isn’t just about understanding the theory; it’s about rolling up your sleeves and diving into the software.
Choosing the Right Software
There are several software options available for converting 3D scans into CAD models. Some of the popular choices include:
- Geomagic Design X: Known for its powerful reverse engineering capabilities, it’s the go-to software for many professionals.
- MeshLab : An open-source option that offers a wide range of tools for mesh processing.
- Artec Studio 19: A powerful 3D scanning software that offers advanced tools for capturing, editing, and processing 3D models with high precision.
- SolidWorks: A favorite among engineers and designers, it provides robust CAD modeling features.
Choosing the right software depends on your specific needs and budget. It’s like choosing between a sports car and a bicycle—both will get you there, but one might be a bit more thrilling.
Step-by-Step Conversion
Once you’ve got your software ready, here’s a general step-by-step guide to converting 3D scans into CAD models:
- Import the 3D Scan: Load the scan data into your chosen software. It’s like importing an image into Photoshop, but with a few more dimensions to worry about.
- Clean Up the Scan: Remove any unwanted artifacts or noise from the scan. Think of it as dusting off an old book before reading it.
- Generate the Mesh: Create a mesh from the point cloud data. This step involves connecting all those dots we talked about earlier.
- Smooth the Surface: Apply surface reconstruction techniques to create a smooth, polished model. It’s the digital equivalent of buffing a car until it shines.
- Convert to CAD: Use the software’s tools to convert the mesh into a CAD model. This is where the magic—I mean, hard work—happens.
Applications and Future Prospects
Turning 3D scans into CAD models has countless applications across various industries. From automotive design to healthcare, the possibilities are endless.
Automotive and Aerospace
In the automotive and aerospace industries, precision is paramount. Engineers use 3D scans to create detailed CAD models of parts and components, ensuring that everything fits together perfectly. It’s like putting together a jigsaw puzzle, but instead of cardboard pieces, you’re dealing with high-tech materials.
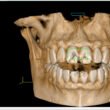
Healthcare and Prosthetics
In healthcare, 3D scanning and CAD modeling are revolutionizing the design of prosthetics and implants. Custom-fit devices can be created with incredible accuracy, improving patient outcomes and comfort. It’s like having a tailor-made suit, but for your body.
Art and Design
Artists and designers are also embracing this technology to create intricate sculptures and installations. The ability to turn a physical object into a digital canvas opens up new creative possibilities. It’s like giving a painter an infinite canvas to work with.
In conclusion, turning 3D scans into CAD models is not just about technology; it’s about transforming the way we design, create, and innovate. As the technology continues to evolve, we can expect even more exciting developments in this field. So, buckle up and get ready for a thrilling ride into the world of 3D modeling.
If you’re eager to explore some amazing 3D models, you can find a treasure trove of them online. Who knows, you might just find the inspiration for your next big project!